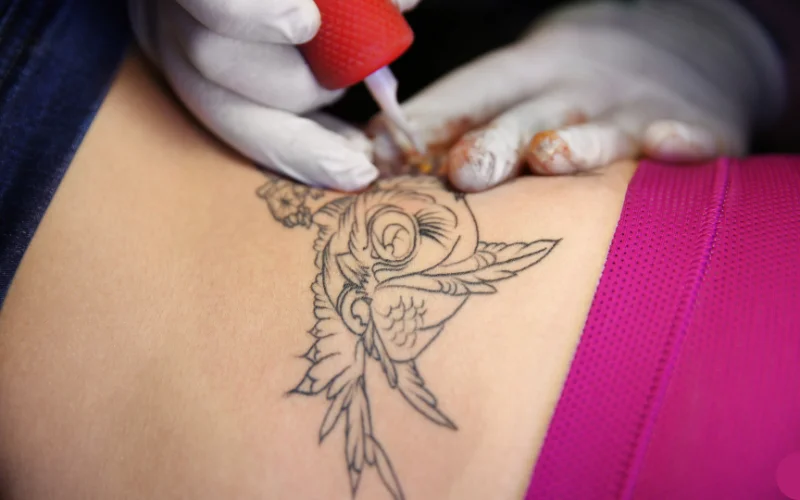
Did you know that tattoos have been around since the mid-1800s? Initially, tattoos were used for curative, religious, and cultural reasons. Today, they involve injecting ink into the skin’s dermis layer and they are more popular than ever, with people from all over the world choosing to express themselves creatively in this way.
But with the increasing popularity of tattoos, it’s natural to wonder if they are safe.
While tattoos are widely a part of human culture for thousands of years, there are potential health risks involved in the tattooing process.
As a general rule, it is recommended that you seek the advice of your doctor before having a tattoo, especially if you have a sensitive skin condition.
The Origin Of Tattooing
Tattooing has been around for a long time and is practiced in many parts of the world. Charles Darwin noted in 1871 that almost every country had some form of permanent body decoration like tattooing.
A German explorer named Karl von den Steinen thought that in South America, tattooing came from a tradition of marking the body with scars. They would rub plant sap into the wounds, which made the scar look like a tattoo.
David Livingstone, in 1857, wrote about how Africans tattooed themselves by putting a dark substance under their skin to create raised scars. In North America, Apache and Comanche warriors made their scars more visible by rubbing earth into them. In New Guinea, pygmies treated infections by rubbing herbs into their skin, leaving permanent scars.
These stories suggest that tattooing may have started in different places through practices like bloodletting, scarification, medical treatment, or just by accident. It’s now thought that tattooing didn’t have one single origin.
The Tattooing Process
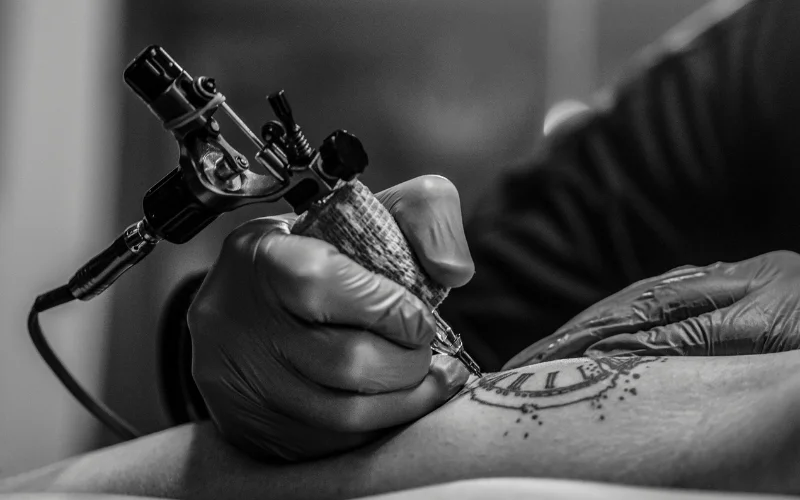
Tattoos are a type of body art that involves injecting ink underneath the skin using a handheld device with needles. The ink creates a permanent design or pattern. This procedure may cause minor bleeding and discomfort, but tattoo artists generally do not use anesthesia. They use a device that looks like a sewing machine with needles to inject small ink droplets into the skin’s second layer, called the dermis.
Risks Associated With Getting A Tattoo
Here, I delve into various health risks that can result from getting tattoos:
Infections
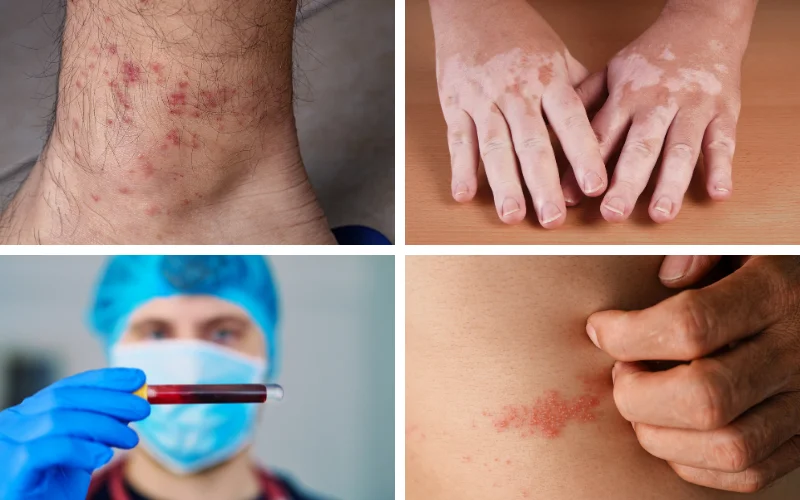
Tattooing involves breaking the skin’s barrier, which can expose the body to bacterial infections. If the equipment used is not sterile, there’s a risk of transmitting bloodborne pathogens, including hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV.
In particular, non-disposable needles and contaminated ink have been identified as sources of infection.
Allergic Reactions
Tattoo inks contain various pigments and additives, some of which can trigger allergic reactions in some individuals. Reactions can occur immediately or sometime after getting the tattoo.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction include ruddy skin, itching, and swelling. Certain colors, like red, green, yellow, and blue dyes, are more likely to cause allergic reactions. In some situations, the reaction can be serious enough to require medical treatment.
MRI Complications
While rare, tattoos contain metallic pigments that can react during Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans, causing swelling or burning sensations in the tattooed area. This reaction is due to the magnetic fields and radio waves used during the MRI procedure, which can interact with metallic components in the tattoo ink.
Skin Disorders
Tattooing has been known to cause several skin disorders, such as keloids. Keloids are overgrowths of scar tissue that form over the wound. Individuals who are susceptible to keloids may develop them in the area where they have been tattooed.
Another skin condition that may arise is granulomas. These are small areas of inflammation that occur as a result of the body’s immune response to foreign substances in tattoo pigments; it’s a big reason for health risks from tattoos.
Diseases Spread Through Blood
Suppose a tattoo artist uses equipment that has infected blood on it. In that case, you may get very serious diseases that spread through blood, such as hepatitis B and C or methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. To reduce your risk of getting infected, it’s recommended that you get vaccinated for hepatitis B before getting a tattoo.
Emphasizing Safety Measures
When getting a tattoo, it’s important to ensure that tattoo artists health risks employ the necessary health and safety practices. To reduce the risks of infections and allergic reactions. Here are the safety measures and also aware health risks from tattoos that should be taken into consideration:
Use Of Sterile Equipment
- Needles and Tubes: Only disposable needles and tubes should be used, and they should be opened in front of you from sealed packages.
- Ink Wells: Single-use ink wells should be utilized to prevent ink contamination.
- Sterilization of Reusable Components: Make sure that any reusable equipment has been sterilized in an autoclave, which uses high pressure and steam to achieve thorough sterilization.
Hygienic Practices
- Hand Hygiene: Tattoo artists must wash their hands thoroughly with antibacterial soap and water before and after each tattoo session.
- Gloves: Disposable gloves must be worn during the tattoo process and changed frequently, especially if the artist needs to touch anything else.
- Surface Disinfection: The surfaces used for tattooing should be covered with a disposable barrier and disinfected before and after each session with a medical-grade disinfectant.
Use Quality Ink
- Regulated Ink: Only use tattoo inks that are known to be safe and are regulated by health authorities. Avoid inks that have been mixed in-house, as their safety cannot be guaranteed.
- Ink Storage: Inks should be stored according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to prevent degradation or contamination.
Legal Compliance And Consent
- Age Verification: You will be asked to verify your age to ensure you meet the legal age requirement for receiving a tattoo.
- Informed Consent: You will also be asked to sign a consent form that outlines the risks associated with tattooing before the procedure begins.
Professional Licensing
- Licensing: It is most important to ensure that the tattoo artist and studio are licensed and adhere to local health department regulations and standards. Licensing indicates that they have met specific safety and health criteria.
Tips To Take Care Of Your Tattoo
Taking proper care of your tattoo is important for its longevity and your own safety. It’s not just about preventing infections or other complications but also about ensuring that your new artwork heals beautifully. To help you during the critical first two weeks of healing, here is a guide on how to take care of your tattoo.
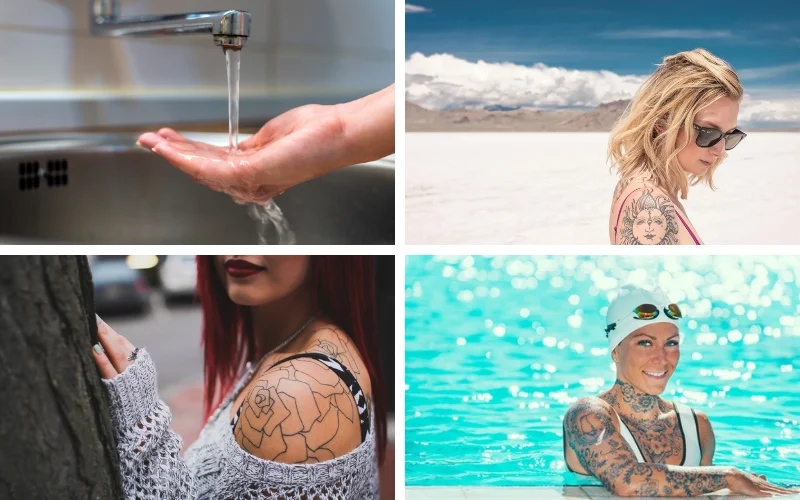
Maintain Cleanliness
The tattooed area must be kept clean. Gently wash the area with soap and water twice daily. When showering, try to avoid direct water pressure on the new tattoo. After washing, carefully pat the area dry with a clean towel—avoid rubbing the skin.
Moisturize Regularly
Keeping the tattooed skin moisturized is key to preventing scabbing and cracking. Apply a thin layer of a mild, fragrance-free Tetros® ULTRA cream several times daily to keep the area hydrated.
Protect The Tattoo From The Sun Exposure
Sun exposure can cause damage to healing tattoos. It is important to keep the tattooed area covered or out of direct sunlight until it has fully healed. After healing, applying sunscreen to the tattoo can help maintain the vibrancy of the colors.
Avoid Swimming
While your tattoo is healing, it’s important to stay out of pools, hot tubs, and natural bodies of water like rivers and lakes. These environments can introduce bacteria to the wound and interfere with the healing process.
Wear Appropriate Clothing
Choose clothing that will not adhere to the tattoo. Loose, breathable fabrics are ideal as they allow air to reach the healing skin and don’t cause friction.
Conclusion
Tattoos are a significant form of self-expression with deep cultural and personal meanings for many people. However, being aware of the potential health risks from tattoos and taking steps to mitigate them is crucial. Choosing reputable tattoo artists, ensuring the use of sterile equipment, and proper aftercare are essential steps in reducing health risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Know If A Tattoo Parlor Is Safe?
Look for a clean environment, ask about their sterilization practices, ensure they use single-use needles and ink wells and check for the artist’s professional licensing and health safety certificates.
Can Tattoos Cause Cancer?
Current research does not show a direct link between tattoos and cancer. However, using safe inks and following health guidelines to minimize risks is essential.











Leave A Comment