The importance of skin barrier repair
- The outermost layer of skin is the stratum corneum
Its primary function is to prevent loss of water from the skin
It contains special lipids: Ceramide, Cholesterol, Palmitic Acid
- They surround the skin cells in a manner that is often described as a bricks and mortar structure
- The bricks are the dormant cells of this layer and the mortar is the special lipids surrounding them. This is referred to as the skin barrier.
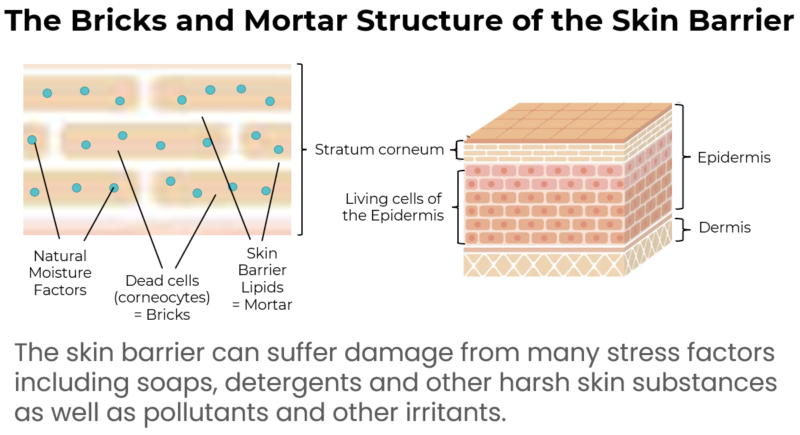
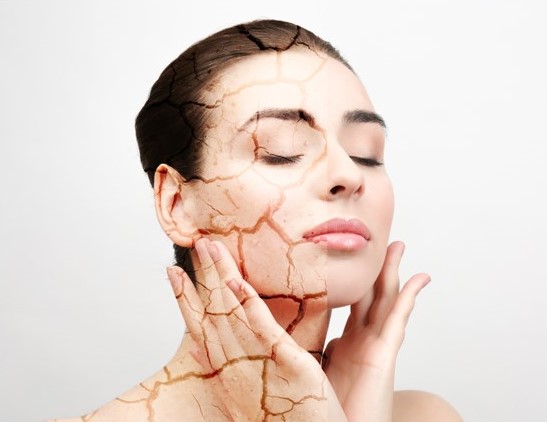
The skin barrier can suffer damage from many stress factors including soaps, detergents and other harsh skin substances, as well as pollutants and other irritants.
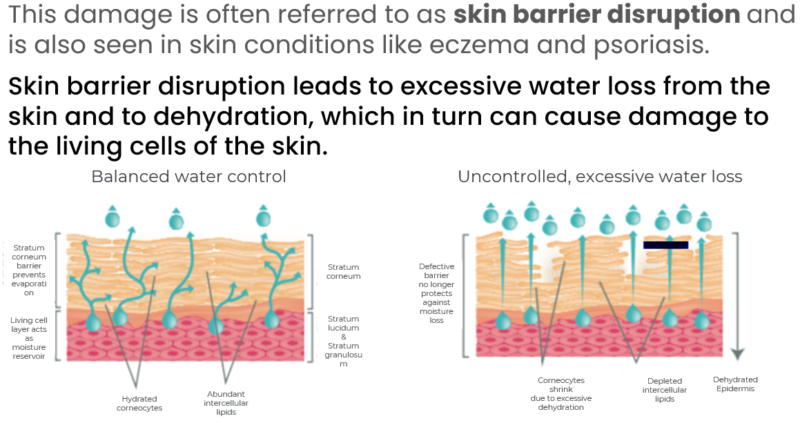
This damage is often referred to as skin barrier disruption and is also seen in skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Skin barrier disruption leads to excessive water loss from the skin and to dehydration, which in turn can cause damage to the living cells of the skin.

Benefits of Taurine
- Osmolyte power to protect skin cell
- Antioxidant free radical scavengers help prevent DNA damage
- Antiglycation effect prevents damage to collagen and elastin
- Antimicrobial properties may help reduce damaging infections
- Photoprotectant effects help mitigate adverse effects of UV radiation
- Helps reduce the adverse effects of inflammation
- Shown to support wound healing
Benefits of TauT activator Hydroxypinacolone retinoate
- Antioxidant properties neutralize damaging free radicals
- Increases production of skin proteins collagen and elastin
- Increases hydration and produces a plumping effect on the skin
- Reduces appearance of excessive and uneven pigmentation
- Reduces excessive skin oil production
Reduces fine lines and wrinkles
Improves acne breakouts and blemishes
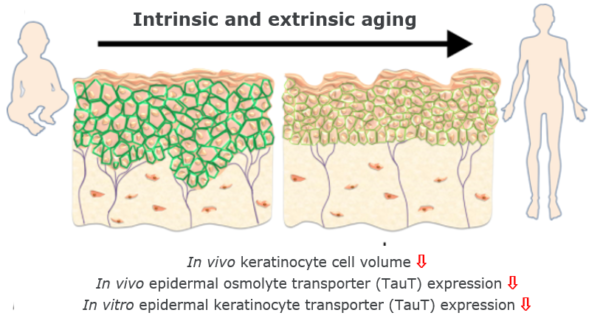
The Importance of Taurine and the Taurine Transporter (TauT)
As our skin ages, skin cells shrink and the function of key water transport systems (TauT) declines
Transport of organic osmolytes, especially taurine is:
- critical to maintaining water balance in the skin
- vital for healthy cellular function
Studies have shown:
a reduction in the size of skin cell
- with age
- after UV exposure
reduced activity of osmolyte transporters (TauT)
- with age
- after UV exposure



