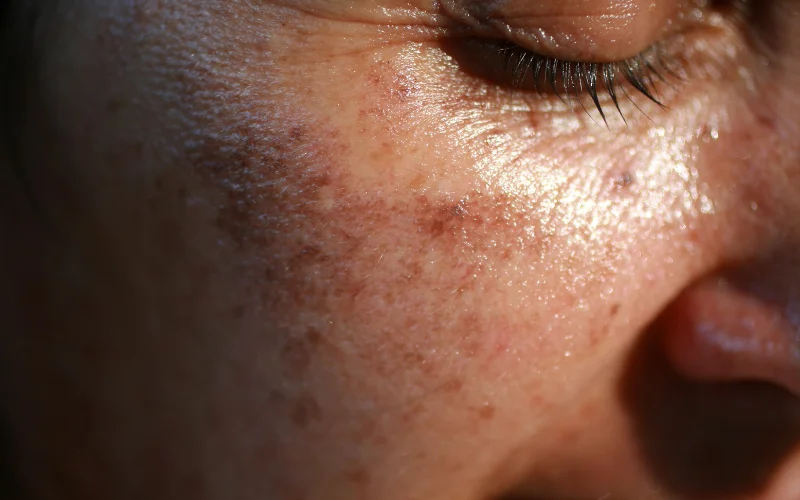
Blotchy skin manifests as irregularly colored or red spots, giving the skin an uneven, patchy appearance. These blemishes vary in shape, size, and color and can be seen on the face, neck, chest, arms, or other parts of the body. The patterns on the affected skin may present as darker, lighter, or redder areas than the normal skin surrounding them.
The types of blotchy skin are diverse and include hyperpigmentation, melasma, hypopigmentation, rosacea, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, which can be caused by sun damage, allergic reactions and hormonal fluctuations. The severity and appearance of blotchy skin can vary widely from person to person, and it may be temporary or persistent condition.
Genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, skincare routines, and environmental stress factors contribute to development of blotchy skin. Effective treatment hinges on pinpointing its underlying cause. A dermatologist or skincare professional can provide guidance on the best course of action, which might involve specific skincare products, treatments, or lifestyle modifications.
Common Characteristics Of Blotchy Skin
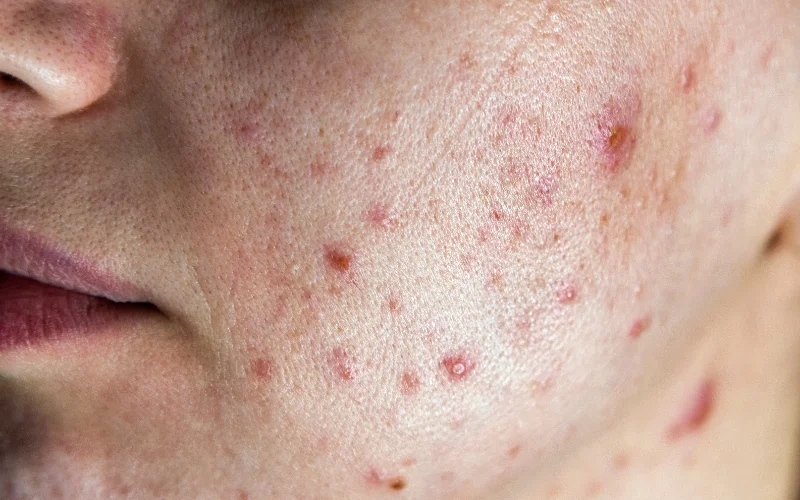
- Red Patches: Often caused by dilation from irritation of blood vessels under the skin.
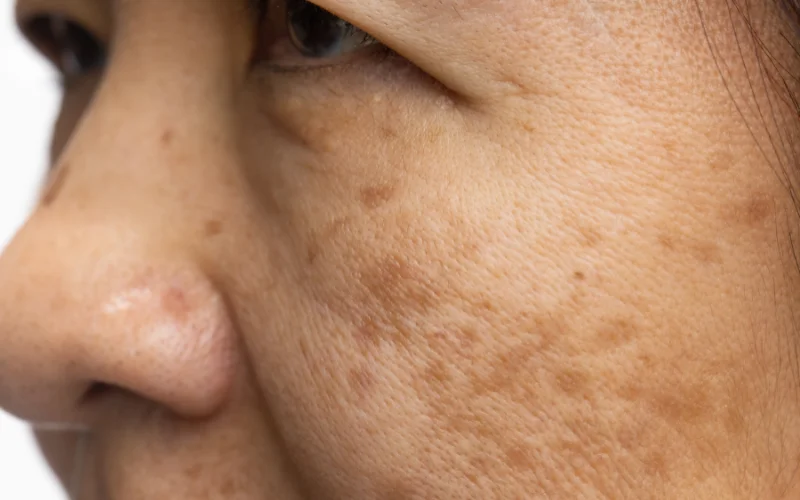
- Brown Spots: Usually due to sun exposure or aging.
- Uneven Skin Tone: Can result from various causes, including sun damage and inflammation
Causes Of Blotchy Skin
Blotchy skin, with its uneven red or brown patches, can be more than a cosmetic concern. It often reflects underlying health conditions or reactions to environmental stressors. Let’s delve deeper into the common causes of blotchy skin and understand these conditions in greater detail.
Environmental Impact
Temperature changes can significantly affect blood circulation in the body. This variation in blood flow can, in turn, lead to alterations in skin color, manifesting as either increased redness with more blood flow or paleness with less.
Exposure To Cold
In cold environments, our body conserves heat by narrowing the small blood vessels in the skin, a process known as vasoconstriction. The reduced blood flow can lead to a pale and sometimes blotchy appearance, as some areas may constrict more than others.
Exposure To Heat
Conversely, in hot conditions, the body tries to release heat through vasodilation, where blood vessels expand. This increased blood flow can cause redness and a blotchy appearance, particularly in areas with more blood vessels close to the skin surface
Management Strategies
- Dress appropriately for the weather to minimize direct skin exposure.
- Use gentle moisturizing products that include ingredients that maintain the skin’s natural barrier.
- Apply sunscreen routinely and stay hydrated, especially in hot weather.
Hormone-Related Changes
Hormonal changes during pregnancy and for other reasons can increase melanin production, developing dark, blotchy patches, often on the face. This condition is known as chloasma or melasma.
Management Strategies
- Make sure to have a sunscreen that protects against UVA and UVB rays. It is recommended to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen to ensure maximum protection .
- Wear wide-brimmed hats for added sun protection.
- Consider using safe skin-lightening agents recommended by a dermatologist.
Common Skin Conditions
Over 85 million people in the United States alone suffer from various skin disorders, and blotchy skin is a common symptom.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Dry, itchy, and inflamed patches of skin mark Eczema. The precise cause is unknown, but it is thought to be primarily due to genetic and environmental factors.
Folliculitis
This condition arises from inflamed hair follicles, often caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. It appears as small, red bumps that may be itchy or painful.
Hives (Urticaria)
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a skin condition characterized by raised, reddish, and itchy welts. They occur due to the body’s reaction to an allergen from sources such as food, medication, insect bites, or pollen. The welts can vary in size and shape and may merge to form larger patches. Hives can appear suddenly; each welt usually lasts a few hours before fading. However, in some cases, hives can persist for several days or weeks, causing discomfort and distress.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin disorder that accelerates the growth of skin cells, leading to inflammation and scaling. It’s associated with other systemic health issues, including arthritis.
Rosacea
Rosacea is a persistent skin ailment that results in redness and prominent blood vessels in the facial region. It is often accompanied by the appearance of tiny, pus-filled bumps, which can cause discomfort and embarrassment.
Sunburn
Sunburn is the skin’s response to excessive UV radiation, leading to red, painful, and sometimes swollen areas.
Management Strategies
- Regular moisturizing and using gentle skincare products are crucial.
- Avoid known triggers (certain foods, stress, allergens).
- Seek medical advice for appropriate topical or systemic treatments.
Tinea Versicolor
Tinea Versicolor is a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the skin’s surface. This overgrowth disrupts the normal pigmentation of the skin, resulting in small, discolored patches that can be lighter or darker than the surrounding skin.
Management Strategies
- Antifungal creams, lotions, or shampoos can be effective.
- In more severe cases, prescription oral antifungal medication may be necessary.
Infections
The skin’s primary function is to protect against diseases and infections. However, certain infections can temporarily overwhelm the skin’s defenses, leading to blotchiness as a noticeable symptom.
Scarlet Fever
This bacterial infection, often following strep throat, leads to a bright red, sandpaper-like rash, fever, and sore throat.
Shingles (Herpes Zoster)
Shingles is a viral infection caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, which is the same virus that causes chickenpox. It typically results in a painful, itchy rash that appears as fluid-filled blisters. The rash usually develops in a single stripe on one side of the body but can also occur on the face or scalp. In addition to the rash, some people may experience other symptoms, such as fever, headache, and fatigue.
Management Strategies
- Scarlet fever requires antibiotic treatment.
- Antiviral medications can reduce the severity of shingles.
Drinking Alcohol
Did you know that wine might cause your face to turn red and blotchy? Wine contains a substance called sulfites, which are used to preserve it. Sulfites can open the small blood vessels in your face more than usual, allowing blood to flow to your skin’s surface more quickly. This can cause redness and blotchiness on your face.
Management Strategies
- Try to avoid excessive consumption of alcohol.
- Instead of alcohol, make a habit of drinking healthy drinks like smoothies, shakes, or water.
How To Diagnose Blotchy Skin
It is important to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis. The dermatologist may use various methods to determine the cause of the condition, such as physical examination, biopsy, or other tests.
- Visual Examination: To identify the pattern and extent of discoloration.
- Medical History: To determine if the condition is related to lifestyle, genetics, or underlying health issues.
- Skin Tests: Sometimes, rule out allergies or specific skin conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment will depend on the underlying cause. Options include:
- Topical Treatments: Should include moisturizers that incorporate ingredients that help to protect and repair the skin barrier as well as having a retinoid and antioxidants.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Improving diet, managing stress, and adopting a suitable skincare routine.
- Medications: Prescription medications may be necessary for conditions like eczema or rosacea.
- Laser Therapy: To address deep pigmentation or vascular issues.
- Sun Protection: Regular use of sunscreen to prevent further damage.
Home Remedies To Prevent Blotchy Skin
Blotchy skin can manifest in various forms, such as redness, dark spots, or an irregular skin tone. It often causes cosmetic concerns and can sometimes be cured through home remedies.
- Natural Masks: Ingredients like turmeric, honey, green tea, or yogurt can be beneficial.
- Hydration: Keeping the skin moisturized to prevent dryness and irritation.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe Vera may be helpful in calming and soothing the skin.
Conclusion
Blotchy skin, while often a cosmetic concern, can sometimes signal underlying health issues. Understanding its causes is the first step toward effective treatment. With the right approach, including lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and preventive care, it is possible to manage and improve the appearance of blotchy skin.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Blotchy Skin Hereditary?
Genetics can sometimes play a role in developing blotchy skin, particularly in conditions like rosacea or certain types of hyperpigmentation.
Can Blotchy Skin Be A Sign Of A Serious Health Issue?
While blotchy skin is often a cosmetic concern, it can sometimes indicate underlying health issues. If blotchy skin is persistent, worsening, or accompanied by other symptoms, it’s important to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis.










Leave A Comment