As we age, our skin undergoes several changes, that may include the development of crepey skin. This condition is characterized by a thin, delicate, and wrinkled texture that resembles crepe paper. Unlike regular wrinkles, which are usually localized to a specific area, crepey skin can affect larger areas of the body and is characterized by a substantial loss of elasticity. This type of skin is commonly observed in female adults, although it can affect people of both sexes at any age.
The Causes Of Crepey Skin
The emergence of crepey skin, characterized by its thin, wrinkled, and delicate texture, can be attributed to several factors, with aging being the primary cause. As we grow, collagen and elastin production decreases, causing skin to lose its firmness and elasticity. This natural process is exacerbated by external or internal factors such as:
Crepey skin and external stress factors
- Sun exposure without adequate protection
- Changes in temperature and wind
- Pollution
- Use of non-cosmetics suitable for your skin
- Superficial dermo-cosmetic treatments
Crepey skin and internal stress factors
- Genetic
- Hormonal changes
- Spicy foods
- Alcohol
- Gluten intolerance
- Stress or intense emotions
Skin stress can be kept under control by reducing these factors as much as possible and by adopting Tetros ULTRA skincare products for stressed skin.
Treatment Options For Crepey Skin
Fortunately, various treatments, from topical treatments to more invasive procedures, are available to improve the appearance of crepey skin.
Topical Treatments
1. Moisturizers and Creams
Daily moisturizers containing ingredients like hyaluronic acid, glycerin, skin barrier lipids and natural moisturizing factors can immediately relieve dryness and improve skin texture. Such ingredients help to draw and lock in moisture.
2. Retinoids
Retinoids (Vitamin A derivatives) are potent agents for reversing the appearance of skin aging. They promote skin cell turnover and stimulate collagen production, reducing the appearance of skin. Prescription retinoids like tretinoin can be more potent, but over-the-counter options like retinol and the more modern hydroxy-pinacolone retinoate are also effective.
3. Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)
Products such as glycolic and lactic acid can promote skin renewal by removing dead skin cells through exfoliation. This can improve skin texture and tone. Just make sure to get your skin products from an authentic source like Tetros Ultra, each product tested by a dermatologist.
Laser Treatments
1. Fractional Laser Therapy
This treatment creates micro-wounds in the skin, triggering the body’s natural healing process and stimulating collagen production. It effectively improves skin texture and elasticity.
2. Intense Pulsed Light (IPL)
IPL treatments can enhance skin texture by promoting collagen production and skin tightening.
Ultrasound Therapy
Ultrasound therapy, uses ultrasound waves to target deeper layers of the skin. The waves heat the targeted tissues, stimulating collagen production. This non-invasive procedure is known for its effectiveness in lifting and tightening the skin.
Cryolipolysis
For crepey skin due to weight loss, cryolipolysis can be effective. This procedure, commonly known as “fat freezing,” helps to remove small fat deposits and tightens the skin. It’s a non-surgical alternative to liposuction.
Fillers and Injectables
Dermal fillers containing hyaluronic acid can plump the skin and reduce the appearance of crepiness. These fillers hydrate the skin due to their water-retaining properties, offering a temporary solution for skin, particularly effective in areas like the hands and face.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels are medical treatments that involve applying a chemical solution to remove the top layers of the skin. This process stimulates the growth of new, smoother, and evenly pigmented skin. Light to medium peels can effectively treat crepey skin, especially on the face, neck, and chest.
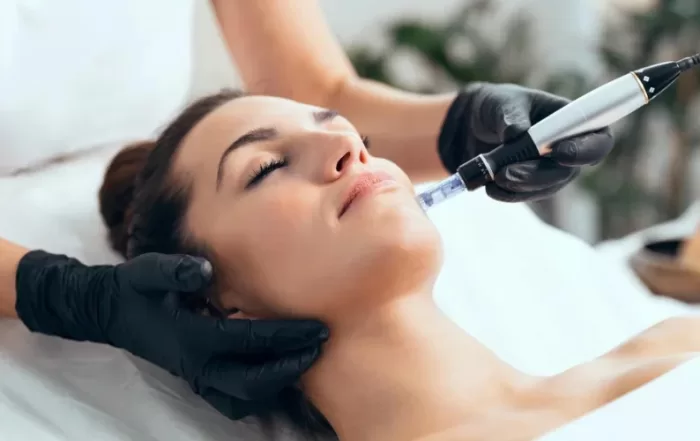
Microneedling
Microneedling is a cosmetic procedure that punctures the skin’s top layer with small needles. This technique triggers the body’s natural healing process, stimulating collagen and elastin production. It can also be combined with topical treatments, such as vitamin C serums or hyaluronic acid, to enhance its effectiveness.
Tips To Prevent Crepey Skin
While you can’t stop the aging process, you can certainly take steps to prevent crepey skin or slow its progression.
- A good moisturizer that contains the optimum combination of moisturizing ingredients helps maintain skin hydration and elasticity.
- Use sunscreen regularly with at least SPF 30. Hats and long sleeves can also protect your skin from UV damage.
- Drinking water keeps your skin hydrated.
- A balanced diet of antioxidants, vitamins C and E, and omega-3 fatty acids can support skin health.
- Quitting smoking can prevent the acceleration of the aging process in your skin.
- Avoid harsh soaps and over-exfoliating, which can strip your skin of essential oils and moisture.
- Quality sleep is critical for skin health. During sleep, the skin undergoes repair and regeneration.
- Try to maintain a stable weight to avoid stretching your skin.
Conclusion
Crepey skin is a common dermatological concern from various factors, primarily aging. While it can be distressing to see changes in skin texture and elasticity, numerous treatment options are available, ranging from over-the-counter creams to professional procedures. Most importantly, preventive measures such as sun protection, hydration, and a healthy lifestyle can significantly delay and minimize its appearance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Is Crepey Skin Different From Regular Wrinkles?
Unlike regular wrinkles, which are usually localized and formed due to muscle movement, crepey skin affects larger areas and is characterized by a general loss of skin elasticity.
Does Diet Affect Crepey Skin?
Yes, a diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients can support skin health and potentially reduce the appearance of crepey skin.
Can Crepey Skin Occur On All Parts Of The Body?
Crepey skin can occur anywhere but is most commonly seen on the neck, chest, arms, and legs.












Leave A Comment